Experience the
Enchanting Wonders of Sri Lanka
every moment is a story waiting to be told.
Are you ready to experience the Vibes?
An Island in Paradise
Inspirations for your next trip
Trending Now

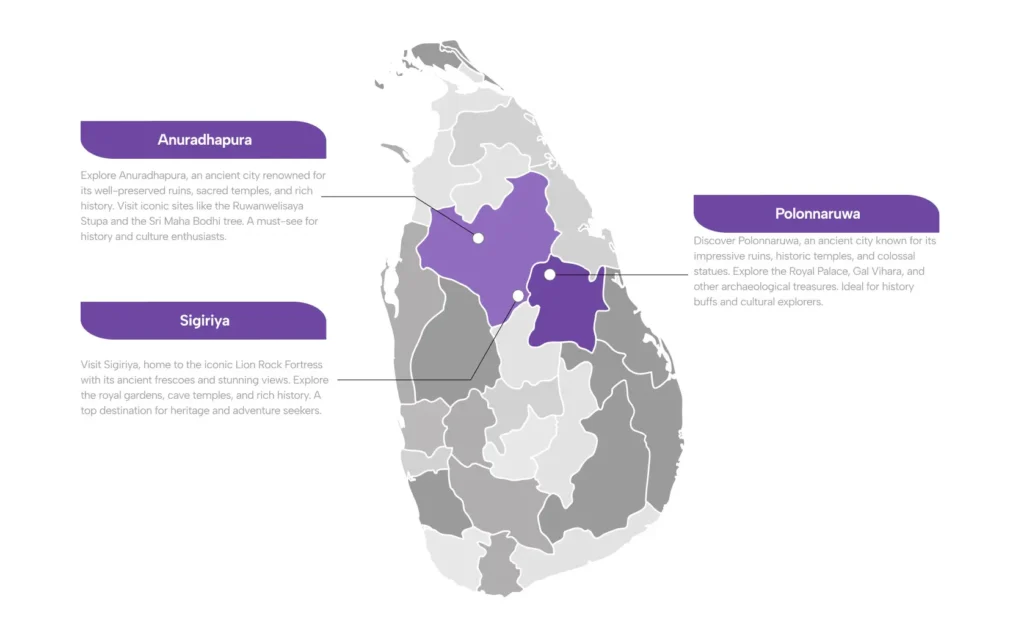
Sigiriya
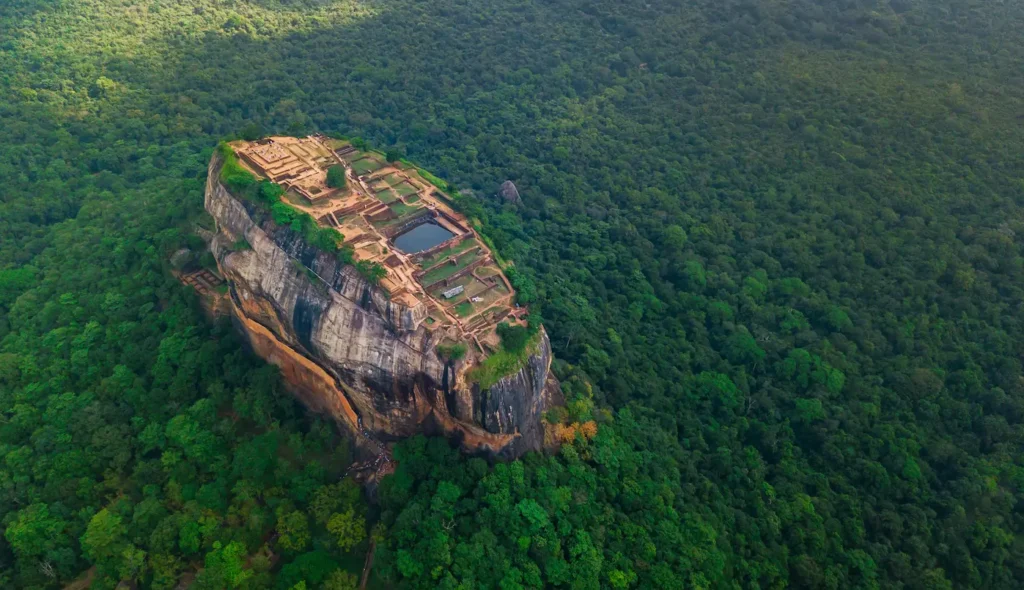

Sigiriya Rock Fortress
Sigiriya, also known as the Lion Rock, is an ancient rock fortress located in the Matale District near the town of Dambulla in the Central Province of Sri Lanka. It is one of the most remarkable historical and archaeological sites in the country and is recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Historical Background:
Sigiriya was built during the reign of King Kasyapa (477 – 495 CE) and served as both a royal residence and a fortress. The site was chosen for its strategic position, and the king transformed it into an elaborate palace complex, showcasing his power and ingenuity. The site later became a Buddhist monastery until the 14th century.
The Rock:
The centerpiece of Sigiriya is a massive column of rock, approximately 200 meters (660 feet) high. The name “Sigiriya” comes from the word “Sihagiri,” meaning “Lion Rock,” which refers to the lion-like shape of the rock’s entrance. Visitors have to ascend a series of steep steps and walkways that lead to the summit, where the ruins of the king’s palace are found.
Architectural and Artistic Significance:
Sigiriya is renowned for its advanced engineering and artistic achievements. The site is surrounded by extensive gardens, water reservoirs, and terraced landscapes, demonstrating sophisticated hydraulic engineering. The rock itself features frescoes depicting beautiful women, known as the “Sigiriya Maidens,” which are some of the best-preserved examples of ancient Sri Lankan art. These frescoes are located in a sheltered gallery along the side of the rock.
Another significant feature is the Mirror Wall, a polished wall on which visitors, over centuries, have inscribed poems and thoughts, some dating back to the 8th century.
The Lion’s Gate:
At the midpoint of the ascent to the summit, there is a platform with the remains of a gigantic lion structure. The entrance to the upper parts of the fortress is through the Lion’s Gate, where two massive lion paws flank the stairway. The lion’s head, which once towered above the entrance, has long since collapsed, but the paws remain and are a key symbol of Sigiriya.
Summit:
The summit of Sigiriya provides a breathtaking view of the surrounding landscape. At the top, the ruins of the royal palace can be found, including the foundations of various buildings, pools, and other structures. The layout suggests that this area was a complex and grandiose place during its time.
Cultural Importance:
Sigiriya is considered one of the most important cultural heritage sites in Sri Lanka, blending architectural innovation, artistic beauty, and historical significance. It is a symbol of the country’s rich history and is a major tourist attraction, drawing visitors from around the world.
Today, Sigiriya stands as a testament to Sri Lanka’s ancient civilization and remains an iconic symbol of the country’s heritage.

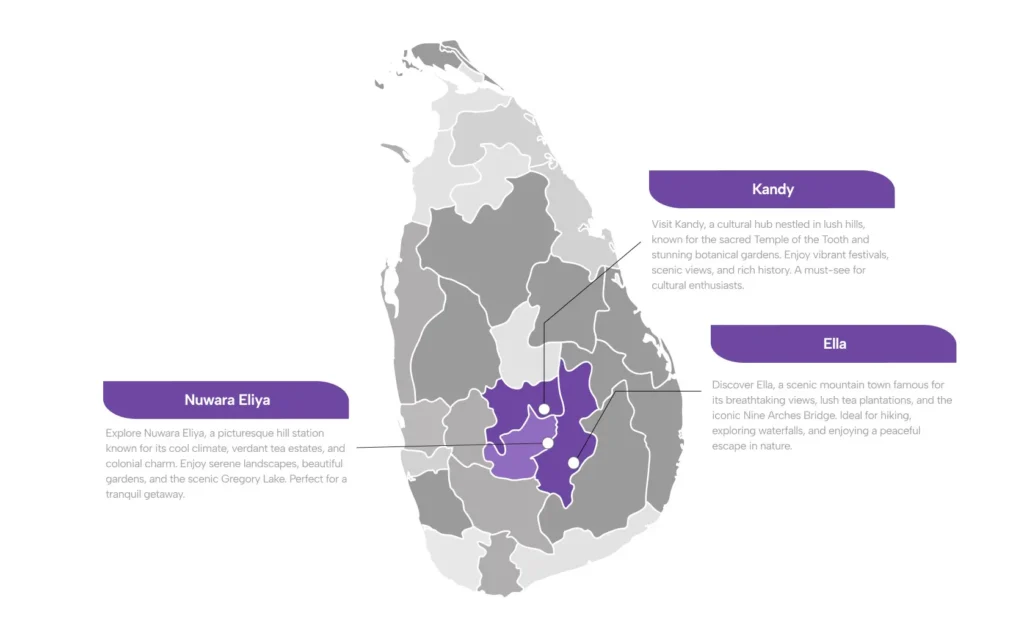
Kandy
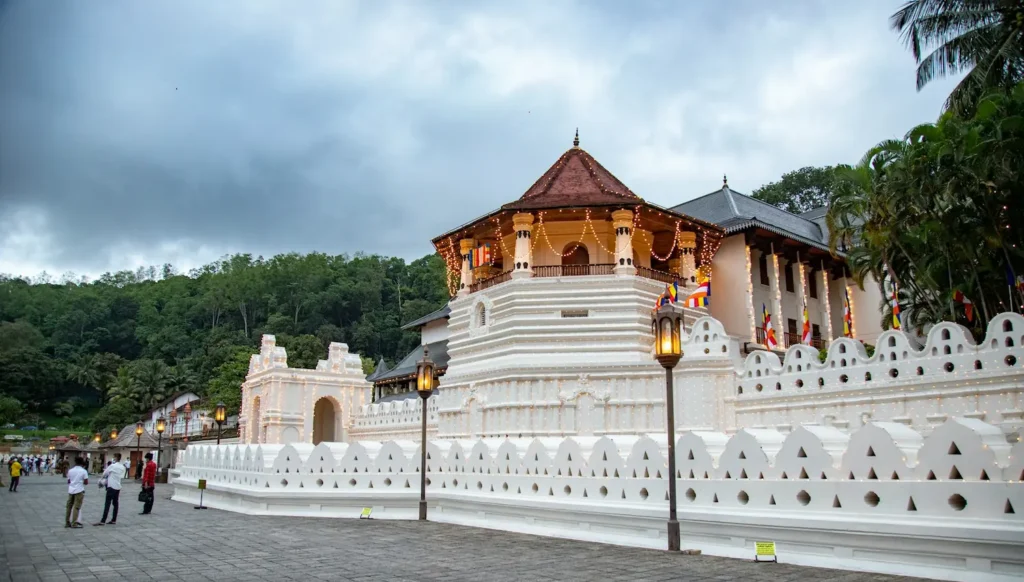

kandy
Kandy, located in the central part of Sri Lanka, is a city of immense historical, cultural, and religious significance. Here’s an overview of its importance:
1. Historical Significance:
- Last Kingdom of Sri Lanka: Kandy was the last independent kingdom in Sri Lanka before it was conquered by the British in 1815. It was the center of resistance against colonial powers for several centuries, preserving Sri Lankan culture and sovereignty.
- Cultural Heritage: Kandy is a UNESCO World Heritage site due to its historical and cultural significance. The city’s architecture, temples, and other historical sites reflect its rich history and its role as the seat of Sinhalese kings.
2. Religious Significance:
- The Temple of the Sacred Tooth Relic (Sri Dalada Maligawa): One of the most sacred Buddhist sites in the world, the Temple of the Sacred Tooth Relic in Kandy houses the relic of the tooth of the Buddha. This relic is deeply revered by Buddhists, and the temple is a major pilgrimage site.
- Esala Perahera: Kandy is famous for the annual Esala Perahera, a grand procession held in honor of the Sacred Tooth Relic. This event attracts thousands of devotees and tourists, featuring traditional Kandyan dancers, drummers, elephants adorned with elaborate garments, and more.
3. Cultural Importance:
- Kandyan Dance: Kandy is the cultural center for traditional Kandyan dance, a classical dance form in Sri Lanka that has been passed down through generations. This dance is an integral part of the city’s identity and is often performed during religious and cultural festivals.
- Traditional Crafts: The city is also known for its traditional crafts, including wood carving, silver and brass work, and batik. These crafts are not only a source of livelihood but also a means of preserving cultural heritage.
4. Geographical Importance:
- Scenic Beauty: Located in the midst of hills, Kandy is surrounded by lush greenery, tea plantations, and natural beauty. The city is built around the Kandy Lake, adding to its picturesque charm. The surrounding region is part of Sri Lanka’s central highlands, known for its biodiversity and scenic landscapes.
- Climate and Agriculture: The region’s climate is cooler than much of Sri Lanka, making it ideal for tea cultivation. Kandy is close to some of the country’s major tea-growing areas, contributing to Sri Lanka’s global reputation as a top tea producer.
5. Modern Significance:
- Education and Research: Kandy is home to several important educational institutions, including the University of Peradeniya, one of the largest and oldest universities in Sri Lanka. The city is a center for research and higher education, particularly in the fields of agriculture, engineering, and the arts.
- Tourism: Kandy is a major tourist destination, attracting visitors from around the world. Its combination of historical sites, cultural richness, and natural beauty makes it a must-visit location in Sri Lanka.

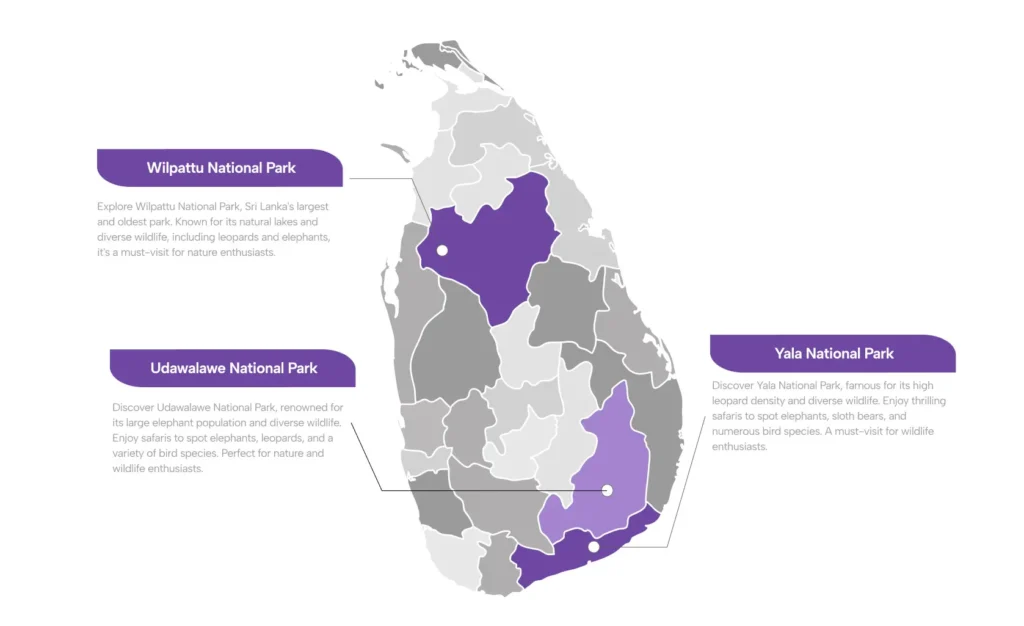
Yala
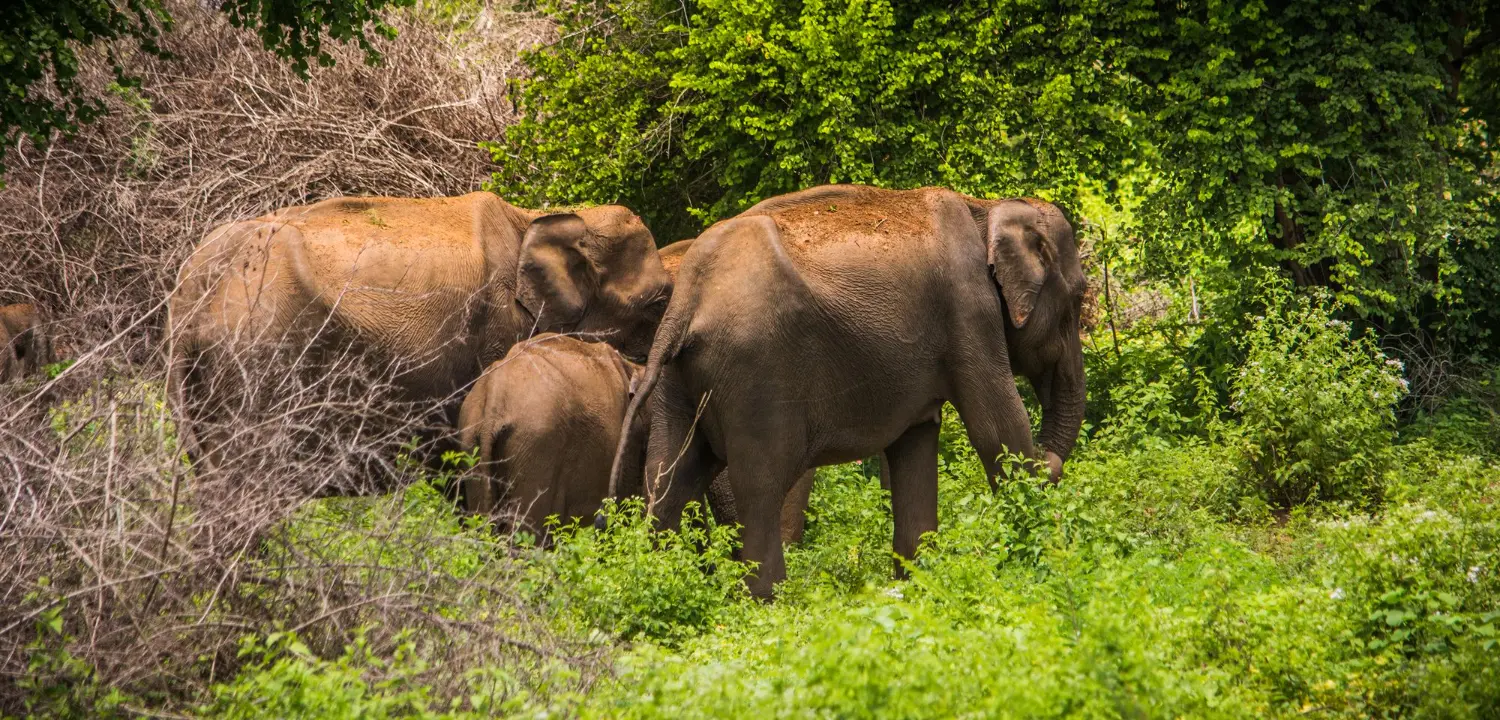

Yala
Yala is one of the most important and well-known national parks in Sri Lanka, offering a unique blend of wildlife, history, and natural beauty. Here’s an overview of its significance:
1. Geographical Location:
- Southern Sri Lanka: Yala National Park is located in the southeastern region of Sri Lanka, spanning the Southern and Uva Provinces. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south, which adds a coastal dimension to the park’s landscape.
2. Wildlife Significance:
- Biodiversity: Yala is the second-largest and most visited national park in Sri Lanka. It is renowned for its rich biodiversity, encompassing a variety of ecosystems including dry monsoon forests, grasslands, wetlands, and coastal areas.
- Leopards: The park is famous for having one of the highest densities of leopards in the world, making it a prime location for leopard sightings. This makes Yala a key destination for wildlife enthusiasts and photographers.
- Other Wildlife: Besides leopards, Yala is home to a wide range of animals, including elephants, sloth bears, spotted deer, sambar deer, wild boars, water buffaloes, and a variety of bird species. It also houses crocodiles, monkeys, and peacocks, making it a hub of Sri Lankan wildlife.
- Bird Watching: The park is a haven for birdwatchers, with over 200 species of birds recorded, including endemic species like the Sri Lanka junglefowl and Sri Lanka grey hornbill.
3. Conservation Importance:
- Protected Area: Yala is a protected area under Sri Lankan law, playing a crucial role in the conservation of the country’s wildlife. It is one of the key areas for biodiversity conservation in Sri Lanka.
- Habitats and Ecosystems: The park supports a variety of habitats, from dense forests to open grasslands and wetlands, each providing a crucial environment for different species. The coastal areas also contribute to marine biodiversity.
- Research and Monitoring: Yala is an important site for research and monitoring of wildlife populations, particularly the leopard. The data gathered here helps in the conservation efforts of endangered species and in maintaining ecological balance.
4. Cultural and Historical Significance:
- Ancient Ruins: Yala is not only significant for its wildlife but also for its historical and cultural heritage. The park contains ancient Buddhist ruins and archaeological sites, some of which date back to the reign of ancient Sri Lankan kingdoms.
- Sithulpawwa Rock Temple: Located within the park, the Sithulpawwa Rock Temple is an ancient Buddhist monastery that dates back over 2,000 years. It is an important pilgrimage site and provides a glimpse into the historical and religious background of the region.
5. Tourism and Economy:</h34
- Tourist Attraction: Yala is a major tourist destination, attracting both local and international visitors. Safari tours are the most popular activity, offering an opportunity to explore the park’s diverse wildlife and natural beauty.
- Economic Contribution: Tourism in Yala contributes significantly to the local economy, providing jobs and income for communities in and around the park. The park’s popularity helps sustain a range of services, including accommodation, guided tours, and transportation.

Turtle Hatchery
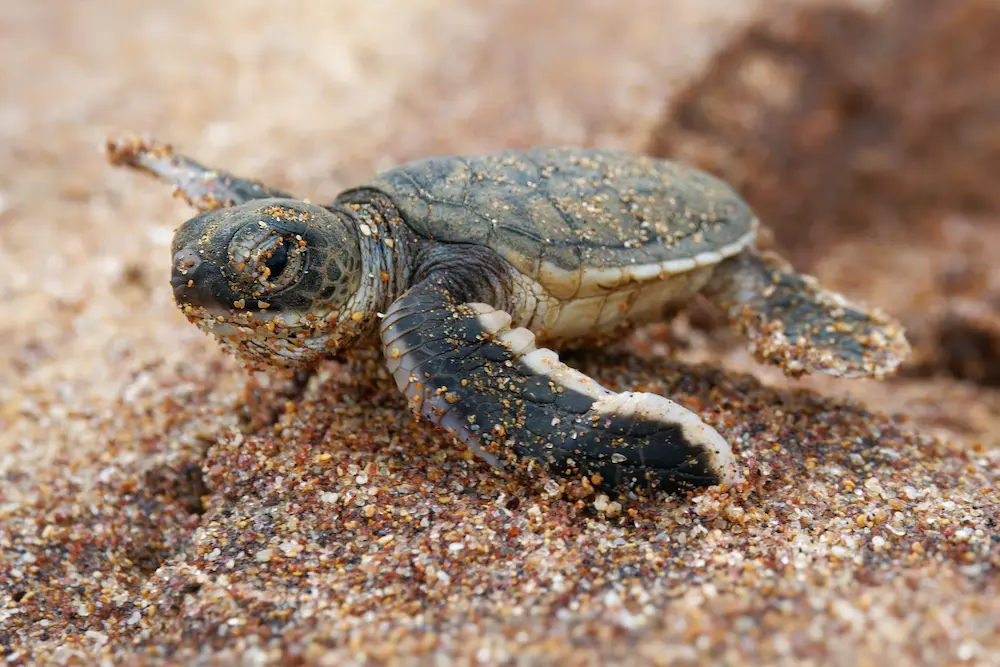

Turtle hatchery
A turtle hatchery in Sri Lanka is a conservation facility dedicated to protecting and rehabilitating endangered sea turtles. These hatcheries play a crucial role in safeguarding turtle eggs from predators, poachers, and environmental threats. Several species of sea turtles, such as the Green Turtle, Leatherback Turtle, Hawksbill Turtle, Loggerhead Turtle, and Olive Ridley Turtle, come to the shores of Sri Lanka to lay eggs.
Turtle hatcheries are critically important for several reasons, especially in the context of sea turtle conservation and broader marine ecosystem health:
1. Protection of Endangered Species:
Many species of sea turtles, including the Green, Hawksbill, and Leatherback turtles, are listed as endangered or critically endangered due to human activities. Turtle hatcheries help safeguard these species by protecting their eggs and ensuring a higher survival rate for hatchlings, which face threats from predators, poaching, and habitat destruction.
2. Combating Poaching and Egg Harvesting:
In many regions, turtle eggs are harvested illegally for food or sold on the black market. Hatcheries protect turtle nests from poachers, reducing the illegal trade of turtle eggs and allowing more eggs to hatch naturally.
3. Increase in Hatchling Survival Rates:
In the wild, very few turtle hatchlings survive to adulthood due to predators, both on land and in the sea. Hatcheries create a controlled environment for the eggs to hatch safely, and many release the hatchlings in a manner that gives them a better chance of surviving their initial, vulnerable stages of life.
4. Environmental Education and Awareness:
Hatcheries serve as educational centers where visitors, including local communities and tourists, can learn about the importance of turtle conservation and marine biodiversity. They promote environmental awareness, responsible tourism, and sustainable practices, which are crucial for the long-term protection of marine life.
5. Support for Scientific Research:
Turtle hatcheries contribute valuable data for research on sea turtle behavior, migration, and population trends. This research is essential for developing better conservation strategies, understanding the effects of climate change on turtle populations, and ensuring their long-term survival.
6. Conservation of Marine Ecosystems:
Sea turtles play an important role in maintaining healthy marine ecosystems. For example, Green Turtles help keep seagrass beds healthy by grazing, and Hawksbill Turtles help control sponges on coral reefs. By conserving turtles, hatcheries indirectly help sustain the balance of marine ecosystems.
In summary, turtle hatcheries are essential for protecting endangered sea turtles, increasing hatchling survival, supporting scientific research, and raising environmental awareness, all of which contribute to the broader goal of marine ecosystem conservation.

Dambulla

Dambulla Rock Fortress
The Dambulla Rock Fortress, also known as the Dambulla Cave Temple or Golden Temple of Dambulla, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of Sri Lanka’s most iconic cultural landmarks. It is located in the central part of the country, near Sigiriya, and is famous for its well-preserved ancient rock caves filled with Buddhist murals and statues.
Key Highlights of Dambulla Rock Fortress:
Historical Significance: The cave complex dates back to the 1st century BCE. King Valagamba of Anuradhapura is credited with transforming these caves into a place of worship during his reign. He sought refuge in these caves after being exiled from his kingdom and, upon regaining power, built a temple to show his gratitude.
Cave Temples: The complex consists of five major caves, each adorned with stunning Buddhist art and statues. The caves contain over 150 statues of Buddha, various deities, and ancient kings. The interior walls and ceilings of the caves are decorated with intricate murals depicting the life of Buddha, including scenes from his journey toward enlightenment.
Architecture and Art: The architecture of Dambulla is remarkable, with the caves carved out of a massive granite rock that towers 160 meters above the surrounding plains. The walls are richly painted with vibrant frescoes and intricate designs, covering an area of more than 2,100 square meters. These murals represent some of the finest examples of ancient Sinhalese art.
Golden Buddha Statue: Near the entrance to the Dambulla complex stands a large golden Buddha statue, which is one of the largest of its kind in Sri Lanka. This striking modern addition complements the ancient caves and is a significant attraction for pilgrims and tourists alike.
Religious and Cultural Importance: Dambulla Rock Fortress remains an active pilgrimage site for Buddhists. The cave temples are considered sacred, with devotees visiting regularly for religious ceremonies and rituals. It has been a center of continuous Buddhist worship for over 2,000 years.
Scenic Location: Dambulla is set amidst lush forests and offers breathtaking views of the surrounding landscape. The hike up to the temple rewards visitors with panoramic vistas, including the nearby Sigiriya Rock Fortress, another famous UNESCO site.
In summary, the Dambulla Rock Fortress is not only a historical and cultural treasure but also a spiritual and artistic marvel, offering insight into Sri Lanka’s rich Buddhist heritage and ancient art. Its combination of religious significance, stunning murals, and architectural grandeur makes it one of the country’s most visited landmarks.

Ravana Falls

Ravana Falls
Ravana Falls is one of the most famous waterfalls in Sri Lanka, located in the Ella region of the Badulla District. The waterfall is named after King Ravana, a prominent figure in the ancient Indian epic, the Ramayana, and is tied to many legends and folklore of the island.
Key Highlights of Ravana Falls:
Mythological Significance: Ravana Falls is deeply connected to the Ramayana epic, in which King Ravana is said to have ruled Lanka (Sri Lanka). According to local lore, Ravana, after abducting Sita, the wife of Lord Rama, is believed to have hidden her in a cave behind the waterfall, known as Ravana Cave. This adds a mythical and historical allure to the falls, making it a significant spot for both locals and visitors interested in the Ramayana.
Location and Accessibility: Ravana Falls is located about 6 kilometers from the town of Ella and is easily accessible from the main road. The waterfall is situated in a lush, mountainous region, surrounded by greenery and rock formations, making it a scenic and popular spot for tourists. The falls are part of the Ravana Ella Wildlife Sanctuary, which adds to the natural beauty and biodiversity of the area.
Waterfall Features: The waterfall is approximately 25 meters (82 feet) in height and cascades down several layers of rock, creating a series of pools at the base. During the rainy season, the falls are particularly impressive, with a strong flow of water, though the waterfall becomes less forceful during the dry season. The cascading water against the rock face provides a stunning visual, especially for photography.
Swimming and Recreation: The pools at the base of Ravana Falls are popular for swimming, especially during the dry season when the water is calm. Visitors often enjoy relaxing in the natural pools, though caution is advised during the rainy season when water levels and currents can become dangerous.
Natural Beauty and Surroundings: The area around Ravana Falls is known for its picturesque landscapes, with lush forests, tea plantations, and mist-covered mountains. It’s a great place for nature lovers and those seeking outdoor activities like hiking. The nearby Ravana Cave and Ravana Ella Temple are also popular attractions that enhance the overall experience of visiting the falls.
In summary, Ravana Falls is not only a beautiful natural wonder but also a site steeped in legend and mythology, making it a must-visit destination in Sri Lanka’s hill country. Its scenic beauty, coupled with its historical and cultural significance, makes it a favorite among tourists and locals alike.
Let’s Plan Your Perfect Trip to Srilanka
Customer Tour Planning
Personalized itineraries and custom travel packages.
Transport Services
Private vehicles, airport pickups, and intercity transfers.
Hotel Bookings
3–5 star hotels and curated luxury accommodations.
Guided Tours & Excursions
Professional guides for sightseeing, cultural tours, adventure activities, and local experiences.
Vibes Quest
Traveler Moments

Vibes Lanka FAQs:
Planning a trip to Sri Lanka? Here are the answers to some of the most common questions our travelers ask.
Discover the rhythms,
Experience the Vibes!

Destinations
Total Customers
User Reviews
Our Happy Customers
The Vibes Sri Lanka trip and experience was totally amazing!! My family and I thoroughly enjoyed each and every day of this trip thanks to Vibes Sri Lanka. The long drives in the comfortable and relaxing seats make it worth it and the service is 10/10. I definitely recommend anyone looking to go with a tour guide, planner and driver to book Vibes Sri Lanka. You will not be disappointed 🤩😎☀️🚐

During my recent Sri lanka visit my entire trip was taken care by Vibes Sri lanka (Sudha and Ruben)! The entire stay, the travel was simply awesome!! Excellent tour operators and I strongly recommend them. They cost less and the service is excellent!! They managed and coordinated 25+ our family members. Made this trip super memorable for all of us.……..

I (with my family) visited Sri Lanka after 25 years in July of 2023. It was our teenage kids first visit to SL. Therefore, we wanted to see the country and visit some family over our short 2 weeks stay. We had a lot to cover within a short period. That’s when our friend introduced us to Sudha from Vibe Sri Lanka. Sudha was excellent in communicating and sorting out our tailor itinerary. He made great suggestions and accommodated us based on what we wanted to see and do.

Our half-day trip to Sigiriya, Sri Lanka, on May 15, 2024, offered an immersive experience into a typical Sinhalese village. The lush greenery and rustic charm of the village surroundings were breathtaking. Our adventure began with a quick stop at a typical village fruit shop, where we enjoyed a delicious king coconut drink, setting the tone for the rest of the tour.







